TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Leading Indicators vs. Lagging Indicators: The Difference
- When to Use Leading Indicators and When to Use Lagging Indicators?
- Risk Analysis and Management
- Challenges When Using Indicators in Technical Analysis
- In-Depth Analysis: Choosing the Right Trading Time and Timeframes
- Contradictory View: Merging Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Developing a Flexible Trading Strategy
In the world of stock trading, when traders face difficult decisions about using leading or lagging indicators, the question arises: Which one is truly useful? Is a lagging indicator the right choice when you want to confirm a trend, or will a leading indicator help you catch price movements quickly? There are no clear answers to these decisions. However, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type of indicator can help you make a reasonable choice.
Leading Indicators vs. Lagging Indicators: The Difference
1. Lagging Indicators
Lagging indicators are tools that traders use to analyze market behavior based on the average of past price data. This means that lagging indicators “smooth” the market data, making it easier to identify trends, but they ignore short-term fluctuations. Sometimes, traders may miss opportunities when the price has already started to move and have to wait for the lagging indicator to confirm the trend, which is not always satisfying.
However, this delay brings reliable confirmation. Some traders believe that although they lose a few pips when entering a trade, it helps them avoid making mistakes from uncertain fluctuations.
Common lagging indicators include:
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
These tools help identify strong trends, but as mentioned, they only work once the trend is confirmed.
2. Leading Indicators
Leading indicators focus on forecasting future price movements. They allow traders to predict potential changes and enter trades early. But this also means you are betting on an uncertain change, as forecasts are not always accurate. Sometimes, a slight reversal can turn the signals given by leading indicators into a “false breakout.”
Common leading indicators include:
- Fibonacci retracement
- Donchian channels
- Support and Resistance levels
These tools primarily help traders enter trades early but require caution, as they may result in “false signals” without confirmation from lagging indicators.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Indicator
As an experienced trader, DLMvn can affirm that no indicator is perfect. Each type has its own advantages and limitations. Using them effectively depends on the trader’s goals and strategy.
| Leading Indicators | Lagging Indicators |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Advantages |
| Provides favorable entry points for potential trades | Provides confirmation, helping traders feel more confident in their decisions |
| Helps enter trades with higher win rates | Reduces the risk of mistakes when identifying trends |
| Disadvantages | Disadvantages |
| Forecasts are not always accurate | May miss opportunities when the market moves before confirmation |
| Requires advanced analysis skills to avoid mistakes | Does not identify key levels like leading indicators |
When to Use Leading Indicators and When to Use Lagging Indicators?
In the stock market, there is no one-size-fits-all formula. These decisions depend on each trader’s trading style and strategy. Traders who prefer short-term, quick trades will favor leading indicators because they provide fast signals to enter a position. However, they must also accept the risks and often set tight stop-loss levels to protect themselves from adverse price movements.
On the other hand, traders with long-term strategies, focused on holding positions for extended periods, will favor lagging indicators. Entering a position late helps them avoid “false signals” and allows for more patience in maintaining their position as the market moves in the direction of a confirmed trend.
Example Illustration: EUR/USD Pair
To illustrate further, DLMvn will share a practical example of using both leading and lagging indicators on the EUR/USD pair. When the market experienced a strong sell-off from the Fibonacci 61.8% level, leading indicators such as Fibonacci and support/resistance channels provided better entry signals. However, when using the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), a lagging indicator, which showed a strong resistance level, the lagging indicator did not immediately provide a sell signal.
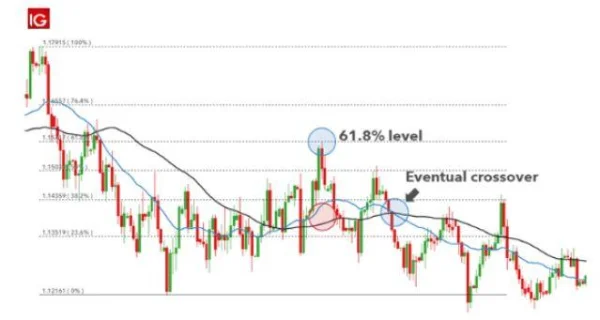
This demonstrates that although lagging indicators do not give early signals, they are very useful for confirming long-term trends. When the 200-day SMA becomes a resistance level, traders can take advantage of this to adjust their trading strategy.
Risk Analysis and Management
Regardless of whether you choose to use leading or lagging indicators, it is crucial to manage risk properly. Leading indicators may provide quick opportunities, but they also push you into uncertain decisions. On the other hand, lagging indicators help protect your trading decisions with solid confirmation, but they are slower in entering the market.
Combining both types of indicators could be the perfect strategy, but determining the right risk-reward ratio is essential. Each strategy may change depending on the currency pair, the trading timeframe, and external factors.
Challenges When Using Indicators in Technical Analysis
While both leading and lagging indicators play important roles in trading strategies, they do not always deliver the expected results. One of the major issues that DLMvn often encounters is over-reliance on these indicators without considering other market factors. Traders sometimes focus solely on technical indicators and overlook the fundamental factors or news events that can strongly impact the market. This can lead to poorly thought-out trading decisions.
1. Contradictory Views
Some traders believe that overusing technical indicators can trap them in “analysis paralysis.” When there are too many conflicting signals from leading and lagging indicators, many traders spend time searching for confirmation from all angles, forgetting that sometimes the market does not follow any rules. Over-analysis can cause them to miss out on good opportunities.
2. DLMvn’s Opinion
Most novice traders tend to be obsessed with technical indicators and seek excessive confirmation from these tools. However, experienced traders understand that indicators are not always reliable. More precisely, lagging indicators may show the market trend after a significant move has occurred, but they do not provide timely opportunities to enter a trade. Meanwhile, leading indicators can give very quick signals, but they are also prone to “false breakouts,” leading to losses if not confirmed by lagging indicators.
In-Depth Analysis: Choosing the Right Trading Time and Timeframes
One important factor that DLMvn wants to emphasize is selecting the right trading timeframe. The choice of indicators depends heavily on the timeframe you trade. For day traders or scalpers, leading indicators can provide quick signals to enter and exit trades within the day. However, for long-term traders, lagging indicators are the ideal tools for confirming trends in the coming weeks or months.
A noteworthy example in the U.S. stock market is the use of lagging indicators like the 200-day SMA. Many long-term traders use this indicator to track large trends. For example, when the 200-day SMA is holding strong support, traders can take advantage of short-term adjustments to increase their position. However, if you rely solely on the SMA and ignore news or fundamental changes in the economy, you may miss out on strong short-term trends.
Contradictory View: Merging Fundamental and Technical Analysis
While many traders still primarily rely on technical analysis, some experts emphasize that fundamental analysis should be considered alongside it for a more comprehensive view of the market. Economic events such as earnings reports, interest rate changes, or central bank meetings can significantly impact market sentiment. In fact, even the best technical indicators cannot withstand the shocks caused by such events.
In some cases, technical indicators may no longer be useful for predicting trends if there are significant fundamental factors at play. For example, when the market receives bad news about the U.S. economy, even if technical indicators like RSI or MACD suggest that the market is oversold, continuing to trade might be a risky decision. In such situations, traders need to carefully weigh both fundamental and technical analysis, rather than relying solely on signals from indicators.
Developing a Flexible Trading Strategy
Another aspect that DLMvn wants to add is the ability to adjust your trading strategy to match the market conditions at any given time. Don’t just “stare” at one set of indicators. The market is always changing, and indicators will have periods of effectiveness and times when they are no longer useful.
Tip: When you see a clear signal from a leading indicator like Fibonacci or support/resistance levels, don’t rush into a trade immediately. Wait for confirmation from lagging indicators or perhaps a signal from the broader market. This approach will help you reduce risk significantly and potentially take advantage of longer-term market trends.
In reality, combining lagging and leading indicators is not always easy. However, when used appropriately, they can help you build a strong and flexible trading strategy.

DLMvn > Trading Indicators > Technical Analysis Indicators Groups: Understanding Their Differences and Applications
Tagged Articles
Essential Technical Indicators Every Trader Should Master
Price Action vs Indicators – Which One Suits Your Trading Style?
Expand Your Knowledge in This Area
Trading Indicators
4 Ways to Leverage Support and Resistance for Optimal Trading
Trading Indicators
Analysis and Trading with the Cup and Handle Pattern
Trading Indicators
Simple Trading Strategy with Support and Resistance
Trading Indicators
Smart Trading With Bullish and Bearish Engulfing Patterns
Trading Indicators
Piercing Line and How to Use It for Market Top/Bottom Reversal in Trading
Trading Indicators
Three Inside & Outside Up Candlestick Patterns: Bullish Reversal Signals