TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What Is The Electronic Communication Network (ECN)?
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of ECN
- Differences Between ECN And Other Trading Forms
- ECN In The Stock Market
- Costs And Fees Associated With ECN
- Types Of ECN Brokers
- Tips For Choosing An ECN Broker
- ECN And Its Impact On The Modern Financial Market
- Potential Risks Of Using ECN
- The Role And Function Of ECN
- Real-World Examples Of ECN
- ECN Brokers
What Is The Electronic Communication Network (ECN)?
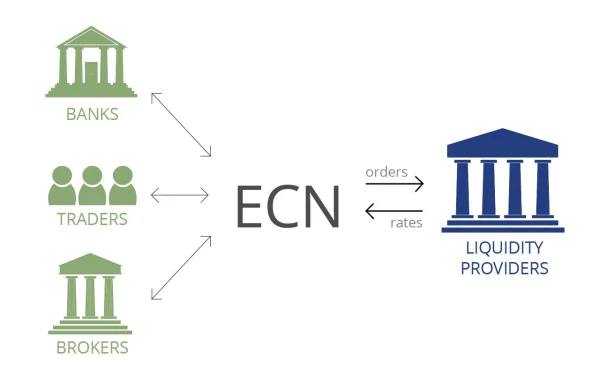
ECN stands for Electronic Communication Network, a tool that provides a direct connection between buyers and sellers in financial markets. The main advantage of ECN lies in enabling fast and transparent trading without requiring intermediaries.
Specific Example: When an investor wants to buy shares of a company like Vinamilk or Hoa Phat but hasn’t found a seller at the desired price, the ECN system will automatically match the investor’s order with a pending sell order at a suitable price. This speeds up the process, ensuring orders are executed accurately and promptly.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of ECN
The ECN network offers numerous essential benefits, including:
- High transparency: Stock prices and buy/sell orders are always publicly available, giving investors more control.
- Fast trading speed: Transactions are processed within milliseconds, which helps limit order delays and increases investment opportunities.
- After-hours trading capability: Investors can execute trades even outside official trading hours, ideal for those needing to process large orders or avoid waiting for the next session.
However, ECN also has some disadvantages:
- High transaction fees: Investors must pay additional commissions when using ECN, which can affect profits, especially with high trading frequency.
- Complexity: For beginners, the ECN system can be challenging to navigate and complex to operate.
Specific Example: Investor A wants to sell shares of a listed company at a price of 100,000 VND/share. Through ECN, A’s sell order is publicly listed so that Investor B—who is looking to buy shares—can see and agree to that price. The trade is then executed quickly.
Differences Between ECN And Other Trading Forms
Unlike traditional methods, ECN allows order matching to occur in a transparent environment without broker interference. In the Market Maker model, brokers may influence the price, whereas ECN prices are purely determined by supply and demand.
Comparison Example: If an investor trades through a Market Maker, the share price received might vary slightly from the market’s actual price due to broker intervention. With ECN, prices are driven by actual supply and demand, enabling a fairer and more transparent process.
ECN In The Stock Market
In the stock market, ECN plays a crucial role in providing fast and transparent trades. Investors who frequently process multiple orders or need to trade after hours often choose ECN to maximize these benefits.
Specific Example: An institutional investor wants to quickly buy a large number of shares in a company due to immediate growth potential. By using ECN, this institution can place a large buy order, and the system will automatically search for suitable sell orders to fulfill it. This minimizes risks and enables the institution to take advantage of opportunities.
Costs And Fees Associated With ECN
One essential factor to consider when using ECN is the transaction fees, which typically include commission fees and trading fees for each order. These costs can significantly impact profits, especially for high-volume traders.
Specific Example: A retail investor using ECN might pay a commission fee of 0.1% per trade. If the investor buys or sells shares worth 500 million VND, the commission would amount to 500,000 VND. This fee should be carefully factored into overall profitability.
Types Of ECN Brokers
Popular types of ECN brokers include:
- Pure ECN: Directly connects buy and sell orders between investors without intermediaries.
- STP (Straight Through Processing): Sends orders directly to liquidity providers without routing them through a market maker.
Recommendation: Investors should choose the type of broker that best matches their trading style. For those requiring fast and frequent trades, Pure ECN is ideal, while STP might be suitable for those looking for favorable prices from multiple sources.
Tips For Choosing An ECN Broker
When selecting an ECN broker, consider factors like reputation, customer service quality, transaction costs, and order matching speed. DLMvn suggests choosing brokers with professional support services and quick response times for the best trading experience.
Example: Before deciding on a broker, investors can check other users’ reviews on investment forums or seek advice from experienced traders. Criteria like low transaction fees and fast customer support are often highly regarded by investors.
ECN And Its Impact On The Modern Financial Market
ECN has brought greater transparency and fairness to both individual and institutional investors, creating a more efficient and less manipulated trading environment. According to research by financial organization XYZ, since the emergence of ECN, bid-ask spreads have significantly narrowed, providing retail investors a fairer opportunity to participate in the market.
Potential Risks Of Using ECN
Although ECN offers many advantages, some risks include:
- Significant price volatility during low trading hours, which could lead to large losses.
- Reduced liquidity in certain circumstances.
- Technical risks: Occasional technical failures, such as network congestion or software glitches, may disrupt trading.
Specific Example: An investor places a sell order during a low-activity period. Share prices may fluctuate sharply, causing a potential loss if there aren’t enough buyers. It is advisable for investors to be cautious during these hours to minimize risk.
The Role And Function Of ECN
ECN creates a fair trading environment for all investors, ensuring fast and accurate order matching. Retail investors also have the opportunity to interact with large institutional orders without intermediaries.
Real-World Examples Of ECN
In reality, major securities companies have adopted ECN to provide modern trading platforms for investors. Leading brokers like DLMvn Securities have developed their ECN systems to serve stock investors in domestic markets.
ECN Brokers
In summary, ECN is an ideal trading tool for those who want transparent and fair trading in the stock market.

DLMvn > Glossary > Electronic Communication Network (ECN): An Effective Connection Tool for Investors
Expand Your Knowledge in This Area
Glossary
Federal Open Market Committee Meeting (FOMC Meeting)
Glossary
Quantitative Easing (QE) and What You Need to Know
Glossary
What are Fund Certificates? Key Considerations for Effective Investment
Glossary
Swap Rate, Swap Curve, and Swap Spread: Key Concepts You Need to Know
Glossary
Why Is Economic Growth Important?
GlossaryTrading Indicators
Moving Averages – A Comprehensive Overview