TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What Is the Morning Star Candlestick Pattern?
- Morning Star Doji Candlestick
- How to Identify the Morning Star on the Market
- How to Trade with the Morning Star Pattern
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading with the Morning Star
- The Truth About the Morning Star Pattern in the Market
- The Other Side: When the Morning Star Fails to Reverse
- Factors Affecting the Morning Star Pattern
The Morning Star candlestick pattern is one of the most powerful trend reversal signals that professional traders in global stock markets always look for. Considered an essential tool in technical analysis, the Morning Star has the ability to signal a change in the price trend, especially when the market is in a strong downtrend.
What Is the Morning Star Candlestick Pattern?
The Morning Star is a three-candle pattern that usually appears when the market is in a strong downtrend. When this pattern forms, it signals that the downward momentum is weakening, and the likelihood of a reversal to an uptrend is very high. Therefore, it becomes one of the crucial indicators traders use to identify entry points for long positions in the market.
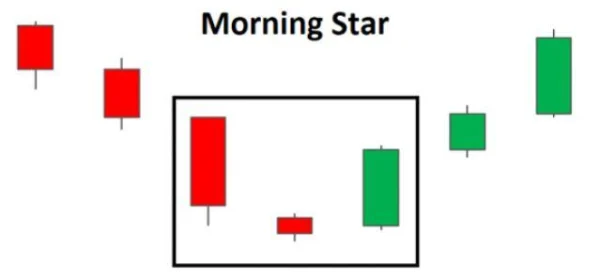
The first candle in this pattern is a strong bearish candle, indicating complete dominance of the selling side. The second candle may be a Doji or at least a small candle, showing market hesitation as the selling pressure decreases. Finally, the third candle is a long bullish candle, indicating the return of buying pressure and confirming a new uptrend.
Morning Star Doji Candlestick
The Doji candlestick, which often appears in the Morning Star pattern, is an important sign when the market has paused after a strong sell-off. When the market closes and opens at nearly the same price, it shows hesitation, and this is when the “bulls” begin to gain control, stop selling, and look for buying opportunities. The next bullish candle confirms this reversal and opens up an opportunity for trading with a new trend.
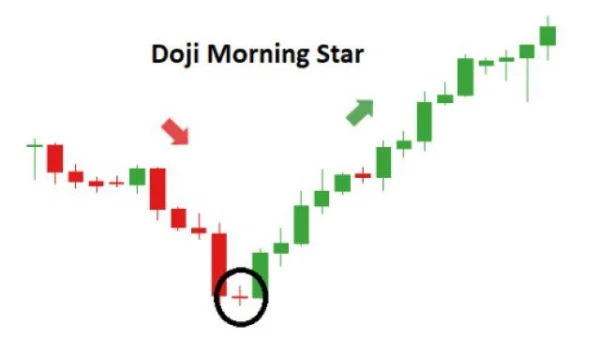
How to Identify the Morning Star on the Market
Identifying the Morning Star pattern is not just about recognizing three candles. To succeed, traders need to combine it with the analysis of prior price action and understand the context in which this pattern appears.
1. Identifying the Current Downtrend
The first candle in the Morning Star pattern is a strong bearish candle, reflecting the strength of the selling force in the current downtrend. At this point, traders should not rush to enter long positions but focus on short trades instead. Entering a buy order at this stage could be risky because the downtrend is still dominant.
2. The Second Candle – Market Hesitation
The second candle can be a small candle or even a Doji. Whether it is bullish or bearish, this candle represents the weakening of the downtrend. It shows that the market is pausing and may be preparing for a reversal. However, it is important not to rush, as the market has not yet made a clear decision.
3. The Third Candle – Confirming the Reversal
The third candle is a critical element in confirming the Morning Star pattern. This is a strong bullish candle, indicating the return of buying pressure and the formation of a new uptrend. At this point, traders can enter a long position, expecting a market reversal.

How to Trade with the Morning Star Pattern
Once the Morning Star pattern has been identified, traders can enter a long position after the third candle closes, i.e., when the market opens with the next candle. However, for cautious traders, instead of rushing in, they may choose to wait for additional confirmation from subsequent price action to be more certain. This approach, however, may cause them to miss out on opportunities, especially in fast-moving markets.
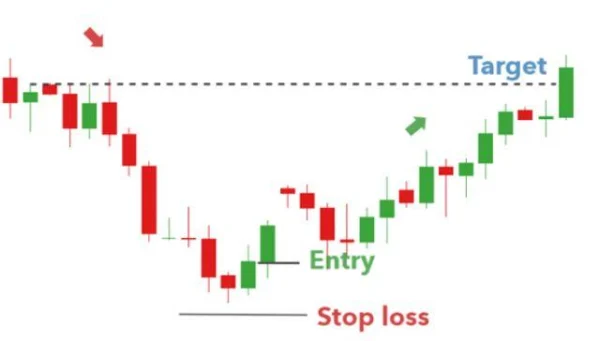
Trade targets can be set at nearby resistance levels, while the stop loss point can be placed below the lowest point of the pattern. It is important to note that nothing is guaranteed in financial markets, so implementing a sound risk management strategy is always crucial to protect investment capital.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading with the Morning Star
Advantages
The Morning Star pattern is relatively easy to identify and apply. It frequently appears in the stock market, especially during strong downtrends, making it easy for traders to find trading opportunities. Both entry and exit points are clearly defined, allowing traders to act quickly and effectively.
Disadvantages
Like any reversal pattern, the Morning Star is not always accurate. One of the biggest risks when trading with this pattern is the failure of the reversal. The market may continue to decline instead of reversing as expected, causing losses for traders who enter long positions too early. Therefore, risk management and having a clear strategy are very important.
When trading with the Morning Star pattern, always remember that there are no absolute guarantees. While this is a strong pattern, the rapid changes in the market can still expose traders to unforeseen risks. Always maintain a clear mindset and trade with caution.
The Truth About the Morning Star Pattern in the Market
The Morning Star is a pattern highly regarded for its simplicity and ease of identification. However, when studying similar patterns across different markets, DLMvn has identified an issue: this pattern does not always produce the strong reversal as expected. In reality, the success rate of the Morning Star can vary significantly depending on the context and the timing of the pattern’s appearance.
For example, in the U.S. stock market during the period 2020-2021, when indices like the S&P 500 experienced frequent fluctuations, the Morning Star pattern appeared quite often during short-term corrections. However, its success rate only reached about 60%, as some of the patterns failed to sustain the uptrend after appearing. This highlights an important reality: while the Morning Star may signal a reversal, it does not always result in a clear continuation.
A typical example is the appearance of the Morning Star pattern on the NASDAQ index in September 2020, when the stock market was facing a deep correction. Despite the clear confirmation of the Morning Star, the index continued to correct and dropped another 10% within a week after that. This shows that the Morning Star pattern does not always guarantee a successful reversal, especially in volatile and unstable markets.
The Other Side: When the Morning Star Fails to Reverse
One point to consider is that the Morning Star does not always provide benefits. Investors, especially beginners, may easily fall into the trap of viewing this pattern as a “sure signal” to enter a buy position. This can lead to significant losses if the pattern is not combined with other factors, such as analyzing the broader trend, resistance and support levels, or even other technical indicators.
One common issue traders face is a lack of patience in confirming the pattern. Especially when the market is uncertain about its trend, the Morning Star may simply be a retracement in a downtrend rather than a sign of a solid reversal. For instance, in October 2018, when the Dow Jones struggled to recover after a sharp sell-off, the Morning Star patterns that appeared could not sustain a long-term uptrend. These patterns were merely temporary corrections in a strong downtrend, and the market continued to fall after that.
Factors Affecting the Morning Star Pattern
It is undeniable that the Morning Star is a powerful pattern in technical analysis, but for a successful trade, traders need to understand the following factors:
-
Trading Volume: An important factor that should not be overlooked when applying the Morning Star pattern is trading volume. If the pattern appears but is not accompanied by strong trading volume, it may just be a temporary retracement. For example, in the case of the S&P 500 in February 2023, when the Morning Star appeared during a short-term decline, low trading volume prevented the pattern from sustaining the uptrend and quickly returned to a downtrend.
-
Economic and Political Environment: The volatility of macroeconomic indicators, such as unemployment rates, interest rates, or political factors, can also influence the success of the pattern. Events such as presidential elections or changes in monetary policy can cause the market to react unpredictably. For instance, in 2022, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy shift created an unstable environment, making reversal patterns like the Morning Star less effective.
-
Market Liquidity: The liquidity of the market is an important factor to consider when trading with patterns like the Morning Star. In markets with low liquidity, the patterns may be affected by external factors, preventing them from performing as expected.

DLMvn > Trading Indicators > Mastering the Morning Star Candlestick to Conquer the Market
Tagged Articles
Profiting from the Morning Doji Star Candlestick Pattern
Expand Your Knowledge in This Area
Trading Indicators
Discover How to Trade Using the Wedge Pattern
Trading Indicators
Analysis and Trading with the Cup and Handle Pattern
Trading Indicators
What Is Price Action? A Basic Guide to Understanding This Method
Trading Indicators
10 Candlestick Patterns Every Trader Should Know
Trading Indicators
4 Ways to Leverage Support and Resistance for Optimal Trading
Trading Indicators
Pitchfork and Its Key Benefits in Trading